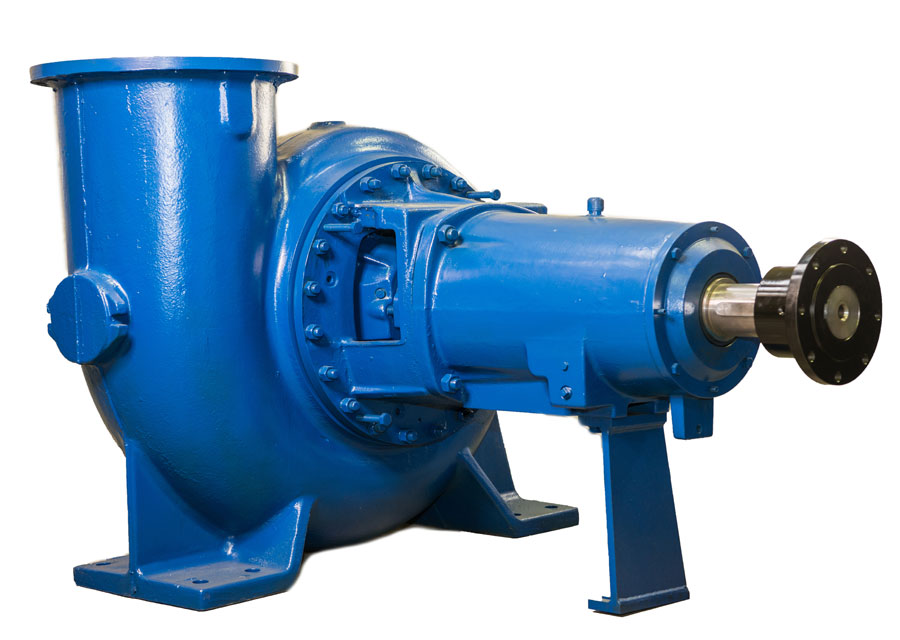
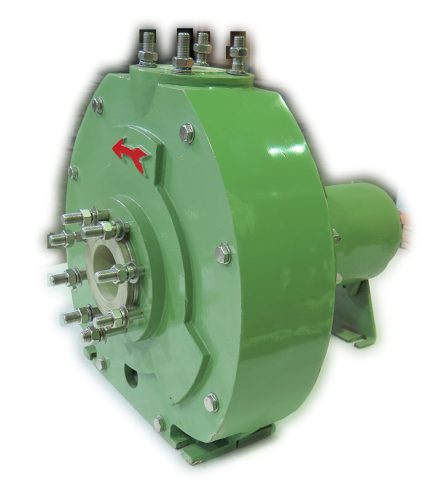
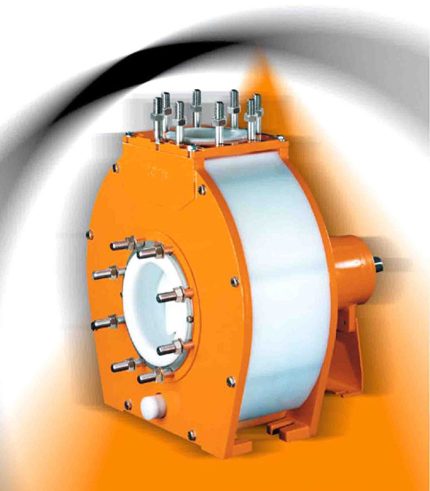
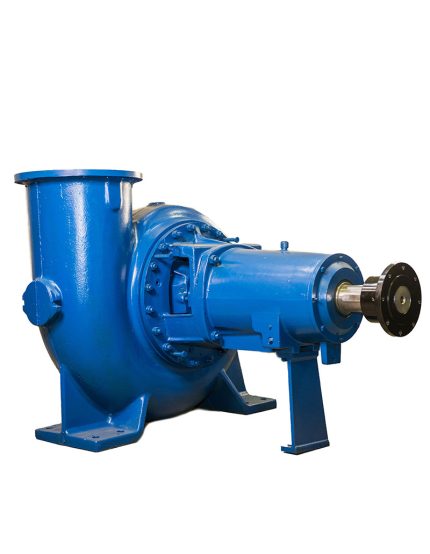
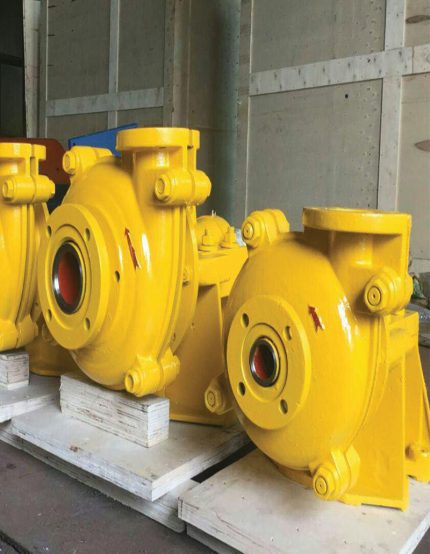
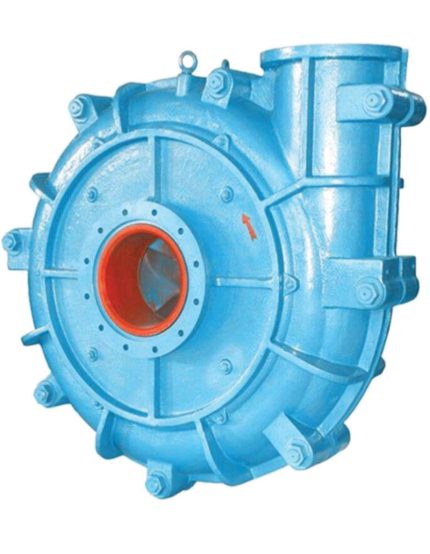
Process pumps are a broad category of pumps used in many different industries to move fluids and semi-solids from point A to point B. Applications for these pumps include moving water, chemicals, mud, or other substances.
What does a process pump include?
While there are many types of process pumps, most have the same basic components. A typical system will include a prime mover, such as a gas-powered engine or an electrical motor. It may also include a gearbox, direct coupled or V-belt drive to help decrease the speed of the pump.